ALZHEIMER'S DISEASE
-
Alzheimer’s disease is the most common age-related neurodegenerative disorder, characterized by the progressive degeneration of neuronal populations and the simultaneous loss of memory and cognitive functions.
SCOPOLAMINE model
Scopolamine, a muscarinic receptor antagonist is widely used to induce cognitive / memory impairment in clinical research (human volunteers) and in experimental animals.
-
Compound testing
Cognitive enhancers are usually tested in this model but other treatments could also be considered. Please feel free to contact us to discuss the feasibility of your study.
-
Endpoints
☐ Percentage of alternation in the T-MAZE (memory performance)
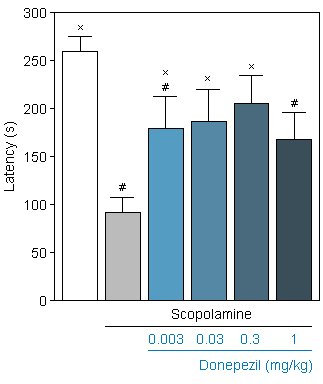
☐ Latency in the PASSIVE AVOIDANCE test
☐ Recognition index in the NOVEL OBJECT RECOGNITION test
-

Deficits induced by scopolamine in 3 mouse strains as assayed in the T-maze -
Reversion of scopolamine-induced deficit by Donepezil (0.003 to 0.3 mg/kg) in Swiss mice in the T-maze.
-

Reversion of scopolamine-induced deficit by Donepezil (0.1 to 0.5 mg/kg) iin Swiss mice in the T-maze. -

Reversion of scopolamine-induced deficit by Nicotine in Swiss mice in the T-maze.
-
Amphetamine : Reversal effect of Amphetamine on cognitive deficit induced by scopolamine in the mouse. Cognitive function was assessed by the ability of mice to perform spontaneous, continuous and sustained alternation in the T-maze. -
Atomoxetine : Reversal effect of Atomoxetine on cognitive deficit induced by scopolamine in the mouse. Cognitive function was assessed by the ability of mice to perform spontaneous, continuous and sustained alternation in the T-maze. -
Caffeine : Reversal effect of Caffeine on cognitive deficit induced by scopolamine in the mouse. Cognitive function was assessed by the ability of mice to perform spontaneous, continuous and sustained alternation in the T-maze.
-
CCMI : Reversal effect of CCMI on cognitive deficit induced by scopolamine in the mouse. Cognitive function was assessed by the ability of mice to perform spontaneous, continuous and sustained alternation in the T-maze. -
Galantamine : Reversal effect of Galantamine on cognitive deficit induced by scopolamine in the mouse. Cognitive function was assessed by the ability of mice to perform spontaneous, continuous and sustained alternation in the T-maze. -
Methylphenidate : Reversal effect of Methylphenidate on cognitive deficit induced by scopolamine in the mouse. Cognitive function was assessed by the ability of mice to perform spontaneous, continuous and sustained alternation in the T-maze.
-
Nicotine : Reversal effect of Nicotine on cognitive deficit induced by scopolamine in the mouse. Cognitive function was assessed by the ability of mice to perform spontaneous, continuous and sustained alternation in the T-maze. -
PNU120596 : Reversal effect of PNU120596 on cognitive deficit induced by scopolamine in the mouse. Cognitive function was assessed by the ability of mice to perform spontaneous, continuous and sustained alternation in the T-maze.
-
-
Reversal of Scopolamine-induced cognitive deficit in the novel object recognition assay by Nicotine. - Scopolamine and/or Nicotine are given at the beginning of the acquisition trial. Retention trial is performed 30 min after the acquisition trial.
Recognition index : proportion of time spent exploring the novel object.
- Scopolamine and/or Nicotine are given at the beginning of the acquisition trial. Retention trial is performed 30 min after the acquisition trial.
You could also be interested in
-
Aged mice
This model is probably the most representative of the human Alzheimer's disease.
Methyllycaconitine
Methyllycaconitine is an α-7 nicotinic acetylcholine receptor specific antagonist with brain penetrance.
-
Amyloid β : animal model
Amyloid-β i.c.v injection induces learning deficits and a dysfunction of the cholinergic system.
Amyloid β : cellular model
Intoxication of neuronal cultures with Aβ has been widely used to understand some of the mechanisms of cell death in AD and thus represents an instrumental in-vitro system to evaluate the efficiency of new drug candidate.

 T-Maze
T-Maze