ALZHEIMER'S DISEASE
-
Alzheimer’s disease is the most common age-related neurodegenerative disorder, characterized by the progressive degeneration of neuronal populations and the simultaneous loss of memory and cognitive functions.
Amyloid-β model
Amyloid-β i.c.v injection induces learning deficits and a dysfunction of the cholinergic system. This model mimics the cognitive deficit associated with Alzheimer’s disease and can be assessed at Neurofit using the passive avoidance test.
-
Compound testing
Disease modifiers are usually tested in this model but other treatments could also be considered. Please feel free to contact us to discuss the feasibility of your study.
-
Endpoints
☐ Latency in the passive avoidance test.
-
Passive avoidance
-
Step through Latency. 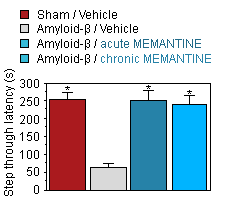
Amyloid-β rats :
Improved learning/memory in Amyloid-β rats treated with Memantine .
Acute and chronic Memantine revert the performance of Aβ rats to the level of Sham specimen.
-
Step through Latency. 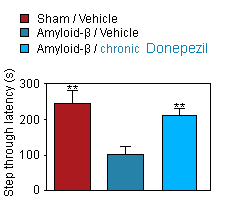
Amyloid-β rats :
Improved learning/memory in Amyloid-β rats treated with Donepezil .
Chronic Donepezil revert the performance of Aβ rats to the level of Sham specimen.
You could also be interested in
-
Novel object recognition
The object recognition task in rodents is considered a test for evaluating working memory in rodents.
Passive avoidance
The Passive Avoidance is a fear-aggravated test used to assess short- or long-term memory.
T-Maze
The T-maze continuous alternation task (T-CAT) is among the method implemented to evaluate the spatial exploratory performance in mice.
-
Aged mice
This model is probably the most representative of the human Alzheimer's disease.
Methyllycaconitine
Methyllycaconitine is an α-7 nicotinic acetylcholine receptor specific antagonist with brain penetrance.
Scopolamine
Scopolamine, a muscarinic receptor antagonist is widely used to induce cognitive / memory impairment in clinical research.
