Passive avoidance
-

-
Presentation
- The Passive Avoidance task is a fear-aggravated test used to assess the short-term and/or long-term memory.
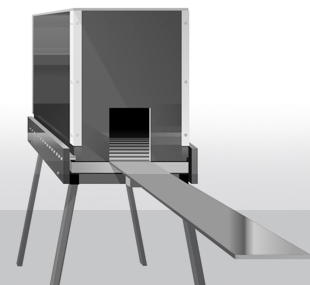
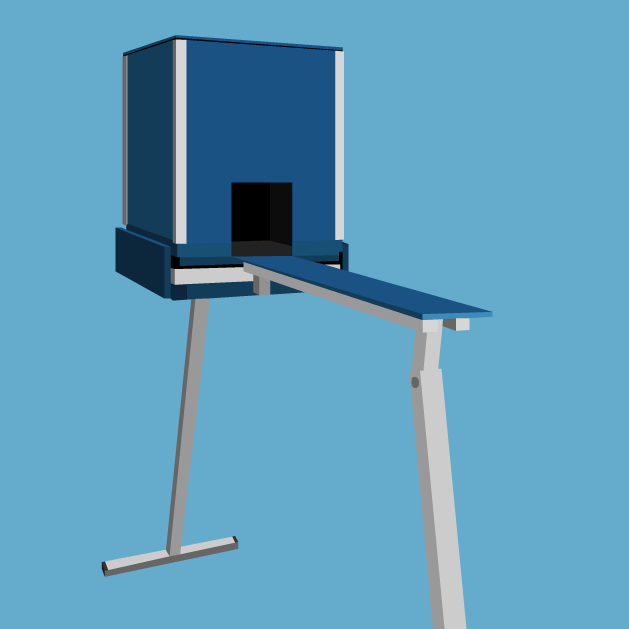
For this test the apparatus is composed of a narrow bridge and a dark compartment at one end. The rodent, following it’s instinct, will naturally choose to enter into the dark box. However, this test requires rodents to act contrary to their innate behaviour.
During the training phase, if the animal enters the dark box, he receives a mild foot shock to indicate that he shouldn’t. In the retention test, the animal is placed at the end of the bridge and if he has learned correctly, he will not enter the dark box as it is paired with the aversive stimulus.
- The Passive Avoidance task is a fear-aggravated test used to assess the short-term and/or long-term memory.
-
Compound testing
Cognitive enhancers or disease modifiers are usually tested in this test but other treatments could also be considered. Please feel free to contact us to discuss the feasibility of your study.
-
Endpoints

Latency time to enter the black box.
-
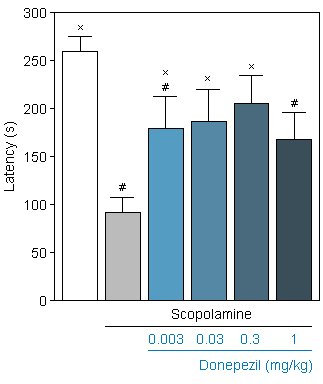
Donepezil : Reversion of Scopolamine-induced cognitive deficit in the Passive Avoidance test in the rat. -
-
Step through Latency. 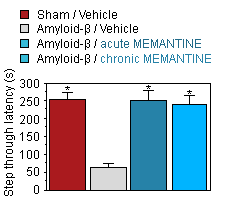
Amyloid-β rats :
Improved learning/memory in Amyloid-β rats treated with Memantine .
Acute and chronic Memantine revert the performance of Aβ rats to the level of Sham specimen.
-
Step through Latency. 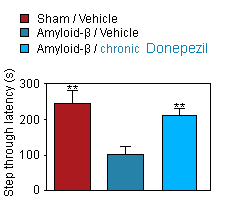
Amyloid-β rats :
Improved learning/memory in Amyloid-β rats treated with Donepezil .
Chronic Donepezil revert the performance of Aβ rats to the level of Sham specimen.
You could also be interested in
-
Novel object recognition
The object recognition task in rodents is considered a test for evaluating working memory in rodents.
T-Maze
The T-maze continuous alternation task (T-CAT) is among the method implemented to evaluate the spatial exploratory performance in mice.
-
Amyloid β (cellular model)
Alzheimer disease is a neurodegenerative disease characterized by an extracellular accumulation of neurotoxic fibrillar amyloid beta peptide.
Neurite outgrowth
Alzheimer’s disease is a common age-related neurodegenerative disorder, characterized by the progressive degeneration of neuronal populations
Scopolamine
Scopolamine, a muscarinic receptor antagonist is widely used to induce cognitive / memory impairment in clinical research and in experimental animals.

 Scopolamine model
Scopolamine model