Experimental Autoimmune Encephalomyelitis (EAE) in Lewis rat
-

-
Presentation
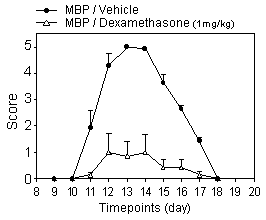
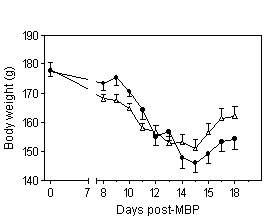
- EAE is a commonly used animal model which shares some degree of similarities with human multiple sclerosis (MS). EAE is induced by CNS antigens such myelin basic protein (MBP) which activates autoreactive T-cells responsible for CNS inflammation and demyelination. Within 10 days after the immunization with MBP of susceptible Lewis rats they develop a progressive weight loss and paralysis that can be assessed using semi-quantitative neurological scoring system.
-
Compound testing
Effect of subchronic or chronic treatment of rats (typically starting before the appearance of first symptom) on:  neurological score until complete recovery
neurological score until complete recovery body weight
body weight
-
Endpoints

Scoring
You could also be interested in
-
RR-EAE
Relapsing/Remitting Multiple Sclerosis is the most frequent form of Multiple Sclerosis.
-
Oligodendrocyte Precursor Proliferation
Multiple Sclerosis is a chronic demyelinating disease of the central nervous system.

 Dexamethasone model
Dexamethasone model